Mic Cues
Mic cues allow you to play live audio through QLab, using the same cueing, routing, and audio effects that are available to Audio cues. The source of this live audio can be any audio input available to your Mac, including the built-in microphone, the mic/line input jack, inputs on a connected audio interface, or incoming Dante or AVB channels. Mic cues run indefinitely (until they are stopped, of course) unless you give them a finite duration.
macOS Security
macOS requires you to proactively grant permission to each program that wants to use any microphone or audio input device in order to limit sneakiness and make it harder for programs to spy on you. You will need to grant QLab permission for microphone access in order to use Mic cues. If you’re not automatically prompted to do this the first time you try, or if you need to change QLab’s permission, you can do that by visiting System Settings → Privacy & Security → Microphone, finding QLab in the list, and flipping the switch on or off.
The Inspector for Mic Cues
When a Mic cue is selected, the inspector shows the Basics tab and Triggers tab, used by all cues, as well as the following tabs:
The I/O Tab
The I/O tab lets you configure the cue’s audio source and destination, as well as the number of channels used by the cue.
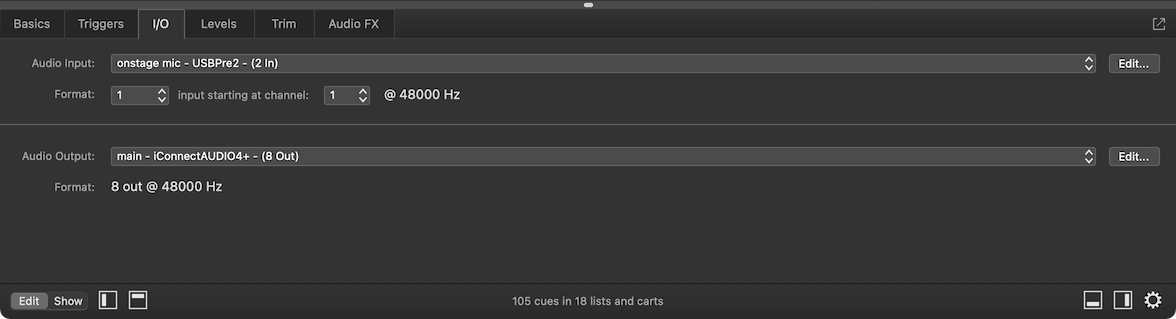
Audio Input. This pop-up menu allows you to select an audio input patch for the cue to use as the source of audio in the cue. Clicking on the menu allows you to select one of the audio input patches already configured in the workspace, or (unpatched) if you want to deliberately prevent the cue from passing any audio when it’s started. You can also choose Open Audio Settings to edit patch list… to quickly get to Workspace Settings → Audio → Audio Inputs, or choose New patch with audio device to quickly generate a new audio input patch and select it for use.
The Edit… button also opens Workspace Settings → Audio → Audio Inputs.
Format. This pair of pop-up menus allow you to configure the input channels of the cue. The first menu sets the number of channels, which can be anywhere from 1 to the number of input channels available in the audio input patch, up to a maximum of 24. In the screen shot above, you can see that the audio input patch uses a device with two inputs, so for this cue, the number of input channels could be 1 or 2. The second menu sets the number of the first input that the cue should use, which can be anywhere from 1 to the number of input channels available.
Audio Output. This pop-up menu allows you to select an audio output patch for the cue to use. Clicking on the menu allows you to select one of the audio output patches already configured in the workspace, or (unpatched) if you want to ensure that the cue does not play when started. You can also choose Open Audio Settings to edit patch list… to quickly get to Workspace Settings → Audio → Audio Outputs, or choose New patch with audio device to quickly generate a new audio patch and select it for use.
The Edit… button opens the audio output patch editor for the currently selected audio output patch, for quick access.
Format displays the number of channels and sample rate of the audio device used by the selected audio output patch. Note that for virtual audio devices such as Existential Audio’s BlackHole or the venerable Soundflower, the sample rate may not display accurately at all times, or even at all. Virtual devices are not always able to provide this information; it’s not necessarily a sign of a problem.
Using different devices for input and output
In QLab 5, Mic cues (and Camera cues) can use different audio devices for incoming audio and outgoing audio. In order to compensate for differences in clocking and sample rates between the input and output device, QLab applies a synchronization algorithm which guarantees that the maximum drift between audio input and audio output stays within a very small, predicable range. The range is defined by this simple equation:
Maximum drift ≤ (buffer size of input audio device) + (buffer size of output audio device) + (very small safety margin)1
A two-hour test2 which recorded audio passing through QLab using this algorithm measured the total range of drift between the input and output between 0 and 3 milliseconds. That’s not nothing, to be sure, but it’s comfortably below the threshold of human perception for most use cases.
The Levels Tab
The Levels tab behaves the same as the Levels tab for Audio cues.
The Trim Tab
The Trim tab behaves the same as the Trim tab for Audio cues.
The Audio FX Tab
The Audio FX tab behaves the same as the Audio FX tab for Audio cues.
Broken Mic Cues
Mic cues can become broken for the following reasons:
No microphone access
QLab has not been given permission to access audio inputs. To clear this warning, open System Preferences → Security & Privacy, then click on the Privacy tab and select Microphone from the list on the left. Then, find QLab in the list on the right and check the box next to it. This step typically does not need to be repeated, but may need to be if you completely uninstall and then reinstall QLab or perform a major macOS version update on your Mac.
Audio input patch does not have enough input channels
The cue has been configured to use more channels than the input device has available. Either select an audio input patch which uses a device with enough input channels, or reduce the number of channels used in the cue to clear this warning.
Missing cue audio effect
The cue has an audio effect assigned, but that AudioUnit is not installed. Either remove the audio effect from the cue or install the missing AudioUnit to clear this warning.
No audio input patch
The cue has no audio input patch assigned. Assign an audio input patch to clear this warning.
Issue with audio input patch
The cue has an audio input patch assigned, but something is wrong with it. The audio input patch will have warnings of its own, listed in the Warnings tab of the Workspace Status window, which you can use to figure out what’s wrong with it. Either fix the audio input patch or select a new audio input patch to clear this warning.
No audio output patch
The cue has no audio output patch assigned. Assign an audio output patch to clear this warning.
Issue with audio output patch
The cue has an audio output patch assigned, but something is wrong with it. The audio output patch will have warnings of its own, listed in the Warnings tab of the Workspace Status window, which you can use to figure out what’s wrong with it. Either fix the audio output patch or select a new audio output patch to clear this warning.
License required
An audio license is required to use Mic cues. Install an audio license or remove the cue to clear this warning.
- The “very small safety margin” is determined by CoreAudio, the low-level macOS framework that QLab uses for everything audio-related, and is not a specific value that QLab can know. It is larger for devices that use higher sample rates and bit depths, and smaller for lower sample rates and bit depths, and in any case it truly is quite small; somewhere in the sub-millisecond range.↩
- In this test, the output device was set to 24-bit depth at a 48 kHz sample rate, and the input device was set to 24-bit depth at a 44.1 kHz sample rate. The devices were each configured to use their own internal clock, and were not configured as an aggregate audio device.↩
Still have a question?
Our support team is always happy to help.